网络分析__使用手册(new)_机器学习-阿里云
目录
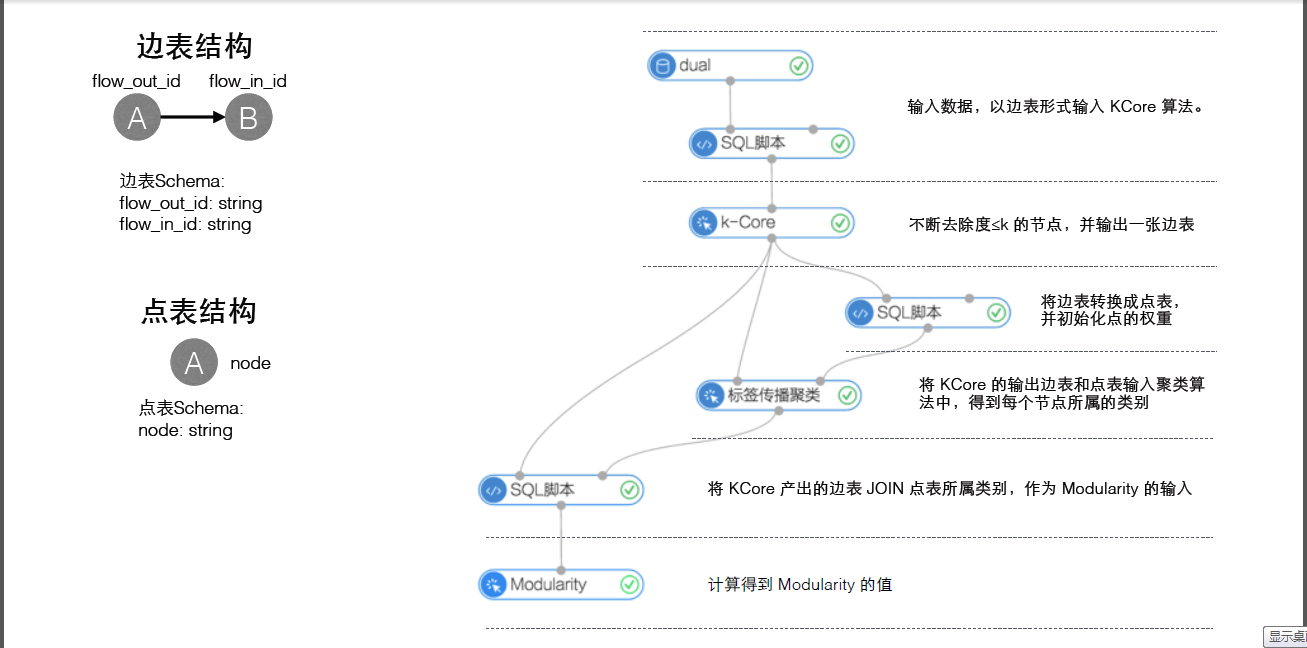
网络分析栏提供的都是基于Graph数据结构的分析算法;下图是使用平台网络分析组件构建的一个分析流程实例:
网络分析栏的算法组件都需要设置运行参数,参数说明如下:进程数:参数代号workerNum,用于设置作业并行执行的节点数;数字越大并行度越高,但框架通讯开销会增大。进程内存:参数代号workerMem,用于设置单个 worker可使用的最大内存量,默认每个worker分配4096内存;实际使用内存超过该值,会抛出OutOfMemory异常。
k-Core
功能介绍
- 一个图的KCore是指反复去除度小于或等于k的节点后,所剩余的子图。若一个节点存在于KCore,而在(K+1)CORE中被移去,那么此节点的核数(coreness)为k。因此所有度为1的节点的核数必然为0,节点核数的最大值被称为图的核数。
参数设置
k:核数的值,必填,默认3
实例
测试数据
新建数据SQL
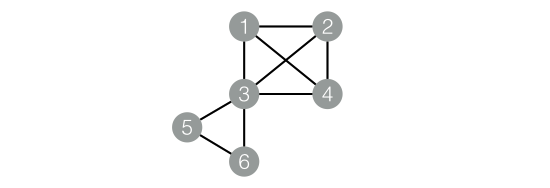
drop table if exists KCore_func_test_edge;create table KCore_func_test_edge asselect * from(select '1' as flow_out_id,'2' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '1' as flow_out_id,'3' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '1' as flow_out_id,'4' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '2' as flow_out_id,'3' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '2' as flow_out_id,'4' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '3' as flow_out_id,'4' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '3' as flow_out_id,'5' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '3' as flow_out_id,'6' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '5' as flow_out_id,'6' as flow_in_id from dual)tmp;
数据对应的graph结构如下图:
运行结果
设定k = 2:运行结果:结果如下:
+-------+-------+| node1 | node2 |+-------+-------+| 1 | 2 || 1 | 3 || 1 | 4 || 2 | 1 || 2 | 3 || 2 | 4 || 3 | 1 || 3 | 2 || 3 | 4 || 4 | 1 || 4 | 2 || 4 | 3 |+-------+-------+
pai命令示例
pai -name KCore-project algo_public-DinputEdgeTableName=KCore_func_test_edge-DfromVertexCol=flow_out_id-DtoVertexCol=flow_in_id-DoutputTableName=KCore_func_test_result-Dk=2;
算法参数
| 参数key名称 | 参数描述 | 必/选填 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| inputEdgeTableName | 输入边表名 | 必填 | - |
| inputEdgeTablePartitions | 输入边表的分区 | 选填 | 全表读入 |
| fromVertexCol | 边表中起点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| toVertexCol | 边表中终点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| outputTableName | 输出表名 | 必填 | - |
| outputTablePartitions | 输出表的分区 | 选填 | - |
| lifecycle | 输出表申明周期 | 选填 | - |
| workerNum | 进程数量 | 选填 | 未设置 |
| workerMem | 进程内存 | 选填 | 4096 |
| splitSize | 数据切分大小 | 选填 | 64 |
| k | 核数 | 必填 | 3 |
单源最短路径
功能介绍
- 单源最短路径参考Dijkstra算法,本算法中当给定起点,则输出该点和其他所有节点的最短路径。
参数设置
起始节点id:用于计算最短路径的起始节点,必填
实例
测试数据
新建数据的SQL语句:
drop table if exists SSSP_func_test_edge;create table SSSP_func_test_edge asselectflow_out_id,flow_in_id,edge_weightfrom(select "a" as flow_out_id,"b" as flow_in_id,1.0 as edge_weight from dualunion allselect "b" as flow_out_id,"c" as flow_in_id,2.0 as edge_weight from dualunion allselect "c" as flow_out_id,"d" as flow_in_id,1.0 as edge_weight from dualunion allselect "b" as flow_out_id,"e" as flow_in_id,2.0 as edge_weight from dualunion allselect "e" as flow_out_id,"d" as flow_in_id,1.0 as edge_weight from dualunion allselect "c" as flow_out_id,"e" as flow_in_id,1.0 as edge_weight from dualunion allselect "f" as flow_out_id,"g" as flow_in_id,3.0 as edge_weight from dualunion allselect "a" as flow_out_id,"d" as flow_in_id,4.0 as edge_weight from dual) tmp;
数据对应的graph结构: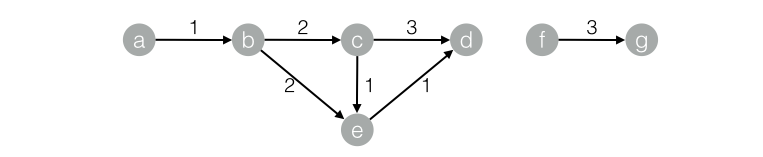
运行结果
结果如下:+------------+------------+------------+--------------+| start_node | dest_node | distance | distance_cnt |+------------+------------+------------+--------------+| a | b | 1.0 | 1 || a | c | 3.0 | 1 || a | d | 4.0 | 3 || a | a | 0.0 | 0 || a | e | 3.0 | 1 |+------------+------------+------------+--------------+
pai命令示例
pai -name SSSP-project algo_public-DinputEdgeTableName=SSSP_func_test_edge-DfromVertexCol=flow_out_id-DtoVertexCol=flow_in_id-DoutputTableName=SSSP_func_test_result-DhasEdgeWeight=true-DedgeWeightCol=edge_weight-DstartVertex=a;
算法参数
| 参数key名称 | 参数描述 | 必/选填 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| inputEdgeTableName | 输入边表名 | 必填 | - |
| inputEdgeTablePartitions | 输入边表的分区 | 选填 | 全表读入 |
| fromVertexCol | 输入边表的起点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| toVertexCol | 输入边表的终点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| outputTableName | 输出表名 | 必填 | - |
| outputTablePartitions | 输出表的分区 | 选填 | - |
| lifecycle | 输出表申明周期 | 选填 | - |
| workerNum | 进程数量 | 选填 | 未设置 |
| workerMem | 进程内存 | 选填 | 4096 |
| splitSize | 数据切分大小 | 选填 | 64 |
| startVertex | 起始节点ID | 必填 | - |
| hasEdgeWeight | 输入边表的边是否有权重 | 选填 | false |
| edgeWeightCol | 输入边表边的权重所在列 | 选填 | - |
PageRank
功能介绍
- PageRank起于网页的搜索排序,google利用网页的链接结构计算每个网页的等级排名,其基本思路是:如果一个网页被其他多个网页指向,这说明该网页比较重要或者质量较高。除考虑网页的链接数量,还考虑网页本身的权重级别,以及该网页有多少条出链到其它网页。 对于用户构成的人际网络,除了用户本身的影响力之外,边的权重也是重要因素之一。例如:新浪微博的某个用户,会更容易影响粉丝中关系比较亲密的家人、同学、同事等,而对陌生的弱关系粉丝影响较小。在人际网络中,边的权重等价为用户-用户的关系强弱指数。带连接权重的PageRank公式为:
 其中,w(i)为节点i的权重,c(A,i)为链接权重,d为阻尼系数,算法迭代稳定后的节点权重W即为每个用户的影响力指数。
其中,w(i)为节点i的权重,c(A,i)为链接权重,d为阻尼系数,算法迭代稳定后的节点权重W即为每个用户的影响力指数。
参数设置
最大迭代次数:算法自身会收敛并停止迭代,选填,默认30
实例
测试数据
新建数据的SQL语句:
drop table if exists PageRankWithWeight_func_test_edge;create table PageRankWithWeight_func_test_edge asselect * from(select 'a' as flow_out_id,'b' as flow_in_id,1.0 as weight from dualunion allselect 'a' as flow_out_id,'c' as flow_in_id,1.0 as weight from dualunion allselect 'b' as flow_out_id,'c' as flow_in_id,1.0 as weight from dualunion allselect 'b' as flow_out_id,'d' as flow_in_id,1.0 as weight from dualunion allselect 'c' as flow_out_id,'d' as flow_in_id,1.0 as weight from dual)tmp;
对应的graph结构: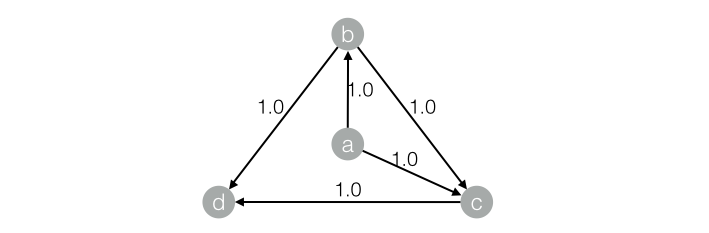
运行结果
结果如下:+------+------------+| node | weight |+------+------------+| a | 0.0375 || b | 0.06938 || c | 0.12834 || d | 0.20556 |+------+------------+
pai命令示例
pai -name PageRankWithWeight-project algo_public-DinputEdgeTableName=PageRankWithWeight_func_test_edge-DfromVertexCol=flow_out_id-DtoVertexCol=flow_in_id-DoutputTableName=PageRankWithWeight_func_test_result-DhasEdgeWeight=true-DedgeWeightCol=weight-DmaxIter 100;
算法参数
| 参数key名称 | 参数描述 | 必/选填 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| inputEdgeTableName | 输入边表名 | 必填 | - |
| inputEdgeTablePartitions | 输入边表的分区 | 选填 | 全表读入 |
| fromVertexCol | 输入边表的起点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| toVertexCol | 输入边表的终点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| outputTableName | 输出表名 | 必填 | - |
| outputTablePartitions | 输出表的分区 | 选填 | - |
| lifecycle | 输出表申明周期 | 选填 | - |
| workerNum | 进程数量 | 选填 | 未设置 |
| workerMem | 进程内存 | 选填 | 4096 |
| splitSize | 数据切分大小 | 选填 | 64 |
| hasEdgeWeight | 输入边表的边是否有权重 | 选填 | false |
| edgeWeightCol | 输入边表边的权重所在列 | 选填 | - |
| maxIter | 最大迭代次数 | 选填 | 30 |
标签传播聚类
功能介绍
图聚类是根据图的拓扑结构,进行子图的划分,使得子图内部节点的链接较多,子图之间的连接较少。标签传播算法(Label Propagation Algorithm, LPA)是基于图的半监督学习方法,其基本思路是节点的标签(community)依赖其邻居节点的标签信息,影响程度由节点相似度决定,并通过传播迭代更新达到稳定。
参数介绍
最大迭代次数:选填,默认30
实例
测试数据
数据生成SQL:
drop table if exists LabelPropagationClustering_func_test_edge;create table LabelPropagationClustering_func_test_edge asselect * from(select '1' as flow_out_id,'2' as flow_in_id,0.7 as edge_weight from dualunion allselect '1' as flow_out_id,'3' as flow_in_id,0.7 as edge_weight from dualunion allselect '1' as flow_out_id,'4' as flow_in_id,0.6 as edge_weight from dualunion allselect '2' as flow_out_id,'3' as flow_in_id,0.7 as edge_weight from dualunion allselect '2' as flow_out_id,'4' as flow_in_id,0.6 as edge_weight from dualunion allselect '3' as flow_out_id,'4' as flow_in_id,0.6 as edge_weight from dualunion allselect '4' as flow_out_id,'6' as flow_in_id,0.3 as edge_weight from dualunion allselect '5' as flow_out_id,'6' as flow_in_id,0.6 as edge_weight from dualunion allselect '5' as flow_out_id,'7' as flow_in_id,0.7 as edge_weight from dualunion allselect '5' as flow_out_id,'8' as flow_in_id,0.7 as edge_weight from dualunion allselect '6' as flow_out_id,'7' as flow_in_id,0.6 as edge_weight from dualunion allselect '6' as flow_out_id,'8' as flow_in_id,0.6 as edge_weight from dualunion allselect '7' as flow_out_id,'8' as flow_in_id,0.7 as edge_weight from dual)tmp;drop table if exists LabelPropagationClustering_func_test_node;create table LabelPropagationClustering_func_test_node asselect * from(select '1' as node,0.7 as node_weight from dualunion allselect '2' as node,0.7 as node_weight from dualunion allselect '3' as node,0.7 as node_weight from dualunion allselect '4' as node,0.5 as node_weight from dualunion allselect '5' as node,0.7 as node_weight from dualunion allselect '6' as node,0.5 as node_weight from dualunion allselect '7' as node,0.7 as node_weight from dualunion allselect '8' as node,0.7 as node_weight from dual)tmp;
数据对应的group结构: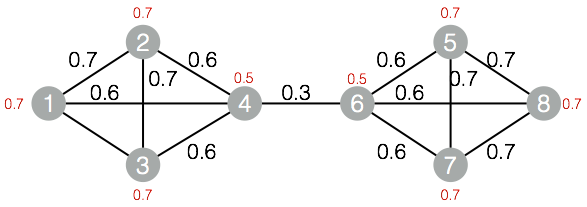
运行结果
结果如下:
+------+------------+| node | group_id |+------+------------+| 1 | 1 || 2 | 1 || 3 | 1 || 4 | 1 || 5 | 5 || 6 | 5 || 7 | 5 || 8 | 5 |+------+------------+
pai命令示例
pai -name LabelPropagationClustering-project algo_public-DinputEdgeTableName=LabelPropagationClustering_func_test_edge-DfromVertexCol=flow_out_id-DtoVertexCol=flow_in_id-DinputVertexTableName=LabelPropagationClustering_func_test_node-DvertexCol=node-DoutputTableName=LabelPropagationClustering_func_test_result-DhasEdgeWeight=true-DedgeWeightCol=edge_weight-DhasVertexWeight=true-DvertexWeightCol=node_weight-DrandSelect=true-DmaxIter=100;
算法参数
| 参数key名称 | 参数描述 | 必/选填 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| inputEdgeTableName | 输入边表名 | 必填 | - |
| inputEdgeTablePartitions | 输入边表的分区 | 选填 | 全表读入 |
| fromVertexCol | 输入边表的起点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| toVertexCol | 输入边表的终点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| inputVertexTableName | 输入点表名称 | 必填 | - |
| inputVertexTablePartitions | 输入点表的分区 | 选填 | 全表读入 |
| vertexCol | 输入点表的点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| outputTableName | 输出表名 | 必填 | - |
| outputTablePartitions | 输出表的分区 | 选填 | - |
| lifecycle | 输出表申明周期 | 选填 | - |
| workerNum | 进程数量 | 选填 | 未设置 |
| workerMem | 进程内存 | 选填 | 4096 |
| splitSize | 数据切分大小 | 选填 | 64 |
| hasEdgeWeight | 输入边表的边是否有权重 | 选填 | false |
| edgeWeightCol | 输入边表边的权重所在列 | 选填 | - |
| hasVertexWeight | 输入点表的点是否有权重 | 选填 | false |
| vertexWeightCol | 输入点表的点的权重所在列 | 选填 | - |
| randSelect | 是否随机选择最大标签 | 选填 | false |
| maxIter | 最大迭代次数 | 选填 | 30 |
标签传播分类
功能介绍
该算法为半监督的分类算法,原理为用已标记节点的标签信息去预测未标记节点的标签信息。
在算法执行过程中,每个节点的标签按相似度传播给相邻节点,在节点传播的每一步,每个节点根据相邻节点的标签来更新自己的标签,与该节点相似度越大,其相邻节点对其标注的影响权值越大,相似节点的标签越趋于一致,其标签就越容易传播。在标签传播过程中,保持已标注数据的标签不变,使其像一个源头把标签传向未标注数据。
最终,当迭代过程结束时,相似节点的概率分布也趋于相似,可以划分到同一个类别中,从而完成标签传播过程
参数设置
阻尼系数:默认0.8收敛系数:默认0.000001
实例
测试数据
生成数据的SQL:
drop table if exists LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_edge;create table LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_edge asselect * from(select 'a' as flow_out_id, 'b' as flow_in_id, 0.2 as edge_weight from dualunion allselect 'a' as flow_out_id, 'c' as flow_in_id, 0.8 as edge_weight from dualunion allselect 'b' as flow_out_id, 'c' as flow_in_id, 1.0 as edge_weight from dualunion allselect 'd' as flow_out_id, 'b' as flow_in_id, 1.0 as edge_weight from dual)tmp;drop table if exists LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_node;create table LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_node asselect * from(select 'a' as node,'X' as label, 1.0 as label_weight from dualunion allselect 'd' as node,'Y' as label, 1.0 as label_weight from dual)tmp;
对应的图结构: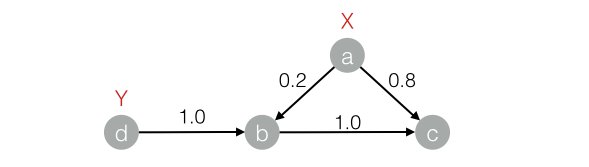
运行结果
结果如下:+------+-----+------------+| node | tag | weight |+------+-----+------------+| a | X | 1.0 || b | X | 0.16667 || b | Y | 0.83333 || c | X | 0.53704 || c | Y | 0.46296 || d | Y | 1.0 |+------+-----+------------+
pai命令示例
pai -name LabelPropagationClassification-project algo_public-DinputEdgeTableName=LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_edge-DfromVertexCol=flow_out_id-DtoVertexCol=flow_in_id-DinputVertexTableName=LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_node-DvertexCol=node-DvertexLabelCol=label-DoutputTableName=LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_result-DhasEdgeWeight=true-DedgeWeightCol=edge_weight-DhasVertexWeight=true-DvertexWeightCol=label_weight-Dalpha=0.8-Depsilon=0.000001;
算法参数
| 参数key名称 | 参数描述 | 必/选填 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| inputEdgeTableName | 输入边表名 | 必填 | - |
| inputEdgeTablePartitions | 输入边表的分区 | 选填 | 全表读入 |
| fromVertexCol | 输入边表的起点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| toVertexCol | 输入边表的终点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| inputVertexTableName | 输入点表名称 | 必填 | - |
| inputVertexTablePartitions | 输入点表的分区 | 选填 | 全表读入 |
| vertexCol | 输入点表的点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| vertexLabelCol | 输入点表的点的标签 | 必填 | - |
| outputTableName | 输出表名 | 必填 | - |
| outputTablePartitions | 输出表的分区 | 选填 | - |
| lifecycle | 输出表申明周期 | 选填 | - |
| workerNum | 进程数量 | 选填 | 未设置 |
| workerMem | 进程内存 | 选填 | 4096 |
| splitSize | 数据切分大小 | 选填 | 64 |
| hasEdgeWeight | 输入边表的边是否有权重 | 选填 | false |
| edgeWeightCol | 输入边表边的权重所在列 | 选填 | - |
| hasVertexWeight | 输入点表的点是否有权重 | 选填 | false |
| vertexWeightCol | 输入点表的点的权重所在列 | 选填 | - |
| alpha | 阻尼系数 | 选填 | 0.8 |
| epsilon | 收敛系数 | 选填 | 0.000001 |
| maxIter | 最大迭代次数 | 选填 | 30 |
Modularity
功能介绍
- Modularity是一种评估社区网络结构的指标,来评估网络结构中划分出来社区的紧密程度,往往0.3以上是比较明显的社区结构。
实例
测试数据
略(与标签传播聚类算法的数据相同)
运行结果
结果如下:+--------------+| val |+--------------+| 0.4230769 |+--------------+
pai命令示例
pai -name Modularity-project algo_public-DinputEdgeTableName=Modularity_func_test_edge-DfromVertexCol=flow_out_id-DfromGroupCol=group_out_id-DtoVertexCol=flow_in_id-DtoGroupCol=group_in_id-DoutputTableName=Modularity_func_test_result;
算法参数
| 参数key名称 | 参数描述 | 必/选填 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| inputEdgeTableName | 输入边表名 | 必填 | - |
| inputEdgeTablePartitions | 输入边表的分区 | 选填 | 全表读入 |
| fromVertexCol | 输入边表的起点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| fromGroupCol | 输入边表起点的群组 | 必填 | - |
| toVertexCol | 输入边表的终点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| toGroupCol | 输入边表终点的群组 | 必填 | - |
| outputTableName | 输出表名 | 必填 | - |
| outputTablePartitions | 输出表的分区 | 选填 | - |
| lifecycle | 输出表申明周期 | 选填 | - |
| workerNum | 进程数量 | 选填 | 未设置 |
| workerMem | 进程内存 | 选填 | 4096 |
| splitSize | 数据切分大小 | 选填 | 64 |
最大联通子图
功能介绍
在无向图G中,若从顶点A到顶点B有路径相连,则称A和B是连通的;在图G种存在若干子图,其中每个子图中所有顶点之间都是连通的,但在不同子图间不存在顶点连通,那么称图G的这些子图为最大连通子图。
参数设置
无
实例
测试数据
生成数据的SQL:
drop table if exists MaximalConnectedComponent_func_test_edge;create table MaximalConnectedComponent_func_test_edge asselect * from(select '1' as flow_out_id,'2' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '2' as flow_out_id,'3' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '3' as flow_out_id,'4' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '1' as flow_out_id,'4' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect 'a' as flow_out_id,'b' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect 'b' as flow_out_id,'c' as flow_in_id from dual)tmp;drop table if exists MaximalConnectedComponent_func_test_result;create table MaximalConnectedComponent_func_test_result(node string,grp_id string);
对应的图结构:
运行结果
结果如下:+-------+-------+| node | grp_id|+-------+-------+| 1 | 4 || 2 | 4 || 3 | 4 || 4 | 4 || a | c || b | c || c | c |+-------+-------+
pai命令示例
pai -name MaximalConnectedComponent-project algo_public-DinputEdgeTableName=MaximalConnectedComponent_func_test_edge-DfromVertexCol=flow_out_id-DtoVertexCol=flow_in_id-DoutputTableName=MaximalConnectedComponent_func_test_result;
算法参数
| 参数key名称 | 参数描述 | 必/选填 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| inputEdgeTableName | 输入边表名 | 必填 | - |
| inputEdgeTablePartitions | 输入边表的分区 | 选填 | 全表读入 |
| fromVertexCol | 输入边表的起点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| toVertexCol | 输入边表的终点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| outputTableName | 输出表名 | 必填 | - |
| outputTablePartitions | 输出表的分区 | 选填 | - |
| lifecycle | 输出表申明周期 | 选填 | - |
| workerNum | 进程数量 | 选填 | 未设置 |
| workerMem | 进程内存 | 选填 | 4096 |
| splitSize | 数据切分大小 | 选填 | 64 |
点聚类系数
功能介绍
在无向图G中,计算每一个节点周围的稠密度,星状网络稠密度为0,全联通网络稠密度为1。
参数设置
maxEdgeCnt:若节点度大于该值,则进行抽样,默认500,选填。
实例
测试数据
生成数据的SQL:
drop table if exists NodeDensity_func_test_edge;create table NodeDensity_func_test_edge asselect * from(select '1' as flow_out_id, '2' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '1' as flow_out_id, '3' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '1' as flow_out_id, '4' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '1' as flow_out_id, '5' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '1' as flow_out_id, '6' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '2' as flow_out_id, '3' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '3' as flow_out_id, '4' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '4' as flow_out_id, '5' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '5' as flow_out_id, '6' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '5' as flow_out_id, '7' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '6' as flow_out_id, '7' as flow_in_id from dual)tmp;drop table if exists NodeDensity_func_test_result;create table NodeDensity_func_test_result(node string,node_cnt bigint,edge_cnt bigint,density double,log_density double);
对应的图结构:
运行结果
结果如下:1,5,4,0.4,1.456572,2,1,1.0,1.246963,3,2,0.66667,1.352044,3,2,0.66667,1.352045,4,3,0.5,1.411896,3,2,0.66667,1.352047,2,1,1.0,1.24696
pai命令示例
pai -name NodeDensity-project algo_public-DinputEdgeTableName=NodeDensity_func_test_edge-DfromVertexCol=flow_out_id-DtoVertexCol=flow_in_id-DoutputTableName=NodeDensity_func_test_result-DmaxEdgeCnt=500;
算法参数
| 参数key名称 | 参数描述 | 必/选填 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| inputEdgeTableName | 输入边表名 | 必填 | - |
| inputEdgeTablePartitions | 输入边表的分区 | 选填 | 全表读入 |
| fromVertexCol | 输入边表的起点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| toVertexCol | 输入边表的终点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| outputTableName | 输出表名 | 必填 | - |
| outputTablePartitions | 输出表的分区 | 选填 | - |
| lifecycle | 输出表申明周期 | 选填 | - |
| maxEdgeCnt | 若节点度大于该值,则进行抽样。 | 选填 | 500 |
| workerNum | 进程数量 | 选填 | 未设置 |
| workerMem | 进程内存 | 选填 | 4096 |
| splitSize | 数据切分大小 | 选填 | 64 |
边聚类系数
功能介绍
在无向图G中,计算每一条边周围的稠密度。
参数设置
无
实例
测试数据
生成数据的SQL:
drop table if exists EdgeDensity_func_test_edge;create table EdgeDensity_func_test_edge asselect * from(select '1' as flow_out_id,'2' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '1' as flow_out_id,'3' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '1' as flow_out_id,'5' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '1' as flow_out_id,'7' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '2' as flow_out_id,'5' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '2' as flow_out_id,'4' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '2' as flow_out_id,'3' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '3' as flow_out_id,'5' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '3' as flow_out_id,'4' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '4' as flow_out_id,'5' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '4' as flow_out_id,'8' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '5' as flow_out_id,'6' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '5' as flow_out_id,'7' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '5' as flow_out_id,'8' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '7' as flow_out_id,'6' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '6' as flow_out_id,'8' as flow_in_id from dual)tmp;drop table if exists EdgeDensity_func_test_result;create table EdgeDensity_func_test_result(node1 string,node2 string,node1_edge_cnt bigint,node2_edge_cnt bigint,triangle_cnt bigint,density double);
对应的图结构:
运行结果
结果如下:1,2,4,4,2,0.52,3,4,4,3,0.752,5,4,7,3,0.753,1,4,4,2,0.53,4,4,4,2,0.54,2,4,4,2,0.54,5,4,7,3,0.755,1,7,4,3,0.755,3,7,4,3,0.755,6,7,3,2,0.666675,8,7,3,2,0.666676,7,3,3,1,0.333337,1,3,4,1,0.333337,5,3,7,2,0.666678,4,3,4,1,0.333338,6,3,3,1,0.33333
pai命令示例
pai -name EdgeDensity-project algo_public-DinputEdgeTableName=EdgeDensity_func_test_edge-DfromVertexCol=flow_out_id-DtoVertexCol=flow_in_id-DoutputTableName=EdgeDensity_func_test_result;
算法参数
| 参数key名称 | 参数描述 | 必/选填 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| inputEdgeTableName | 输入边表名 | 必填 | - |
| inputEdgeTablePartitions | 输入边表的分区 | 选填 | 全表读入 |
| fromVertexCol | 输入边表的起点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| toVertexCol | 输入边表的终点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| outputTableName | 输出表名 | 必填 | - |
| outputTablePartitions | 输出表的分区 | 选填 | - |
| lifecycle | 输出表申明周期 | 选填 | - |
| workerNum | 进程数量 | 选填 | 未设置 |
| workerMem | 进程内存 | 选填 | 4096 |
| splitSize | 数据切分大小 | 选填 | 64 |
计数三角形
功能介绍
在无向图G中,输出所有三角形。
参数设置
maxEdgeCnt:若节点度大于该值,则进行抽样,默认500,选填。
实例
测试数据
生成数据的SQL:
drop table if exists TriangleCount_func_test_edge;create table TriangleCount_func_test_edge asselect * from(select '1' as flow_out_id,'2' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '1' as flow_out_id,'3' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '1' as flow_out_id,'4' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '1' as flow_out_id,'5' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '1' as flow_out_id,'6' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '2' as flow_out_id,'3' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '3' as flow_out_id,'4' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '4' as flow_out_id,'5' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '5' as flow_out_id,'6' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '5' as flow_out_id,'7' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '6' as flow_out_id,'7' as flow_in_id from dual)tmp;drop table if exists TriangleCount_func_test_result;create table TriangleCount_func_test_result(node1 string,node2 string,node3 string);
对应的图结构:
运行结果
结果如下:1,2,31,3,41,4,51,5,65,6,7
pai命令示例
pai -name TriangleCount-project algo_public-DinputEdgeTableName=TriangleCount_func_test_edge-DfromVertexCol=flow_out_id-DtoVertexCol=flow_in_id-DoutputTableName=TriangleCount_func_test_result;
算法参数
| 参数key名称 | 参数描述 | 必/选填 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| inputEdgeTableName | 输入边表名 | 必填 | - |
| inputEdgeTablePartitions | 输入边表的分区 | 选填 | 全表读入 |
| fromVertexCol | 输入边表的起点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| toVertexCol | 输入边表的终点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| outputTableName | 输出表名 | 必填 | - |
| outputTablePartitions | 输出表的分区 | 选填 | - |
| lifecycle | 输出表申明周期 | 选填 | - |
| maxEdgeCnt | 若节点度大于该值,则进行抽样。 | 选填 | 500 |
| workerNum | 进程数量 | 选填 | 未设置 |
| workerMem | 进程内存 | 选填 | 4096 |
| splitSize | 数据切分大小 | 选填 | 64 |
树深度
功能介绍
对于众多树状网络,输出每个节点的所处深度和树ID。
参数设置
无
实例
测试数据
生成数据的SQL:
drop table if exists TreeDepth_func_test_edge;create table TreeDepth_func_test_edge asselect * from(select '0' as flow_out_id, '1' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '0' as flow_out_id, '2' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '1' as flow_out_id, '3' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '1' as flow_out_id, '4' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '2' as flow_out_id, '4' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '2' as flow_out_id, '5' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect '4' as flow_out_id, '6' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect 'a' as flow_out_id, 'b' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect 'a' as flow_out_id, 'c' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect 'c' as flow_out_id, 'd' as flow_in_id from dualunion allselect 'c' as flow_out_id, 'e' as flow_in_id from dual)tmp;drop table if exists TreeDepth_func_test_result;create table TreeDepth_func_test_result(node string,root string,depth bigint);
对应的图结构:
运行结果
结果如下:0,0,01,0,12,0,13,0,24,0,25,0,26,0,3a,a,0b,a,1c,a,1d,a,2e,a,2
pai命令示例
pai -name TreeDepth-project algo_public-DinputEdgeTableName=TreeDepth_func_test_edge-DfromVertexCol=flow_out_id-DtoVertexCol=flow_in_id-DoutputTableName=TreeDepth_func_test_result;
算法参数
| 参数key名称 | 参数描述 | 必/选填 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| inputEdgeTableName | 输入边表名 | 必填 | - |
| inputEdgeTablePartitions | 输入边表的分区 | 选填 | 全表读入 |
| fromVertexCol | 输入边表的起点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| toVertexCol | 输入边表的终点所在列 | 必填 | - |
| outputTableName | 输出表名 | 必填 | - |
| outputTablePartitions | 输出表的分区 | 选填 | - |
| lifecycle | 输出表申明周期 | 选填 | - |
| workerNum | 进程数量 | 选填 | 未设置 |
| workerMem | 进程内存 | 选填 | 4096 |
| splitSize | 数据切分大小 | 选填 | 64 |
最后更新:2016-11-23 16:04:15
上一篇: 文本分析__使用手册(new)_机器学习-阿里云
文本分析__使用手册(new)_机器学习-阿里云
下一篇: 【图算法】金融风控实验__案例_机器学习-阿里云
【图算法】金融风控实验__案例_机器学习-阿里云
 查询签名密钥列表__后端签名密钥相关接口_API_API 网关-阿里云
查询签名密钥列表__后端签名密钥相关接口_API_API 网关-阿里云 Python SDK下载__SDK下载_SDK使用手册_归档存储-阿里云
Python SDK下载__SDK下载_SDK使用手册_归档存储-阿里云 ListVirtualMFADevices__用户管理接口_RAM API文档_访问控制-阿里云
ListVirtualMFADevices__用户管理接口_RAM API文档_访问控制-阿里云 Job配置约定__作业配置说明_使用手册_数据集成-阿里云
Job配置约定__作业配置说明_使用手册_数据集成-阿里云 修改集群名称__集群_API参考_E-MapReduce-阿里云
修改集群名称__集群_API参考_E-MapReduce-阿里云 短信字数最多能发多少个字? 建议400个字以内的短信。__常见问题_短信服务-阿里云
短信字数最多能发多少个字? 建议400个字以内的短信。__常见问题_短信服务-阿里云 自定义算法开发__产品简介_推荐引擎-阿里云
自定义算法开发__产品简介_推荐引擎-阿里云 企业信息安全整体解决方案 阿里云栖大会,我们来了!
企业信息安全整体解决方案 阿里云栖大会,我们来了! 关键组件和流程__产品简介_业务实时监控服务 ARMS-阿里云
关键组件和流程__产品简介_业务实时监控服务 ARMS-阿里云 添加监控服务器__测试环境_使用手册_性能测试-阿里云
添加监控服务器__测试环境_使用手册_性能测试-阿里云
相关内容
 常见错误说明__附录_大数据计算服务-阿里云
常见错误说明__附录_大数据计算服务-阿里云 发送短信接口__API使用手册_短信服务-阿里云
发送短信接口__API使用手册_短信服务-阿里云 接口文档__Android_安全组件教程_移动安全-阿里云
接口文档__Android_安全组件教程_移动安全-阿里云 运营商错误码(联通)__常见问题_短信服务-阿里云
运营商错误码(联通)__常见问题_短信服务-阿里云 设置短信模板__使用手册_短信服务-阿里云
设置短信模板__使用手册_短信服务-阿里云 OSS 权限问题及排查__常见错误及排除_最佳实践_对象存储 OSS-阿里云
OSS 权限问题及排查__常见错误及排除_最佳实践_对象存储 OSS-阿里云 消息通知__操作指南_批量计算-阿里云
消息通知__操作指南_批量计算-阿里云 设备端快速接入(MQTT)__快速开始_阿里云物联网套件-阿里云
设备端快速接入(MQTT)__快速开始_阿里云物联网套件-阿里云 查询API调用流量数据__API管理相关接口_API_API 网关-阿里云
查询API调用流量数据__API管理相关接口_API_API 网关-阿里云 使用STS访问__JavaScript-SDK_SDK 参考_对象存储 OSS-阿里云
使用STS访问__JavaScript-SDK_SDK 参考_对象存储 OSS-阿里云